Superpower countries
Global Nuclear Warhead Distribution by Nation 2024
Published
9 months agoon
A nuclear warhead is an extremely powerful bomb that creates a massive explosion using nuclear energy. Instead of relying on chemical reactions like regular bombs, it gets its power from breaking apart atoms (nuclear fission) or sticking them together (nuclear fusion). This process makes it far more powerful and dangerous than ordinary explosives.
Why Countries keep Nuclear Weapons?
Countries keep nuclear warheads mainly to stop other countries from attacking them. They do this by making the idea of a fight too scary because of the huge damage nuclear weapons can cause. Nuclear weapons also help protect a country from strong enemies and give it an advantage in military matters. Plus, having these weapons can boost a country’s power and influence in international discussions and negotiations. These countries are also known as nuclear power country.
Let’s dive into an interesting analysis of the global nuclear landscape based on the above data on nuclear warheads.
The global nuclear arsenal, distributed among several countries, plays a significant role in international security dynamics, particularly in the context of recent geopolitical tensions. Here’s an analysis incorporating the deployment, testing sites, and the influence of nuclear warheads in current conflicts:
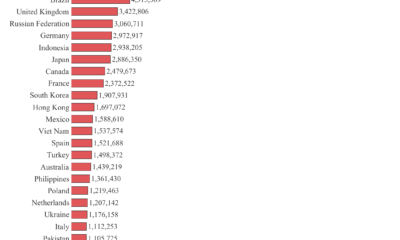
The United States and Russia hold the largest nuclear arsenals, with the U.S. possessing 5,044 warheads (42.7% of the global total) and Russia holding 5,580 (45.4%). These warheads are deployed at key strategic sites like Minot Air Force Base in North Dakota and submarine bases in Murmansk. The U.S. conducted its first nuclear test in Alamogordo, New Mexico, and Russia in Semipalatinsk, Kazakh SSR. These extensive arsenals and their historical testing underscore the continuing relevance of nuclear deterrence, particularly in light of recent conflicts such as the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war. Russia’s nuclear capability looms large as a deterrent against deeper NATO involvement in Ukraine, and the potential for nuclear escalation remains a concern.
China, with 500 warheads (4.1%), has conducted tests at Lop Nur in Xinjiang and maintains a smaller, yet strategically significant, number of deployed warheads. China’s nuclear posture plays a critical role in the broader Asia-Pacific security landscape, particularly in relation to the U.S. and its allies. While the U.S. and China engage in strategic competition, nuclear deterrence remains a stabilizing factor, preventing potential conflicts from escalating.
France and the United Kingdom, with 290 (2.4%) and 225 (1.8%) warheads respectively, have maintained strong nuclear deterrents, with their arsenals deployed on submarines and airbases. France’s testing began at Reggane in French Algeria, while the UK’s was at the Monte Bello Islands in Australia. Both countries’ nuclear forces play key roles in NATO’s collective defense strategy, providing a nuclear umbrella that extends across Europe, especially crucial in the face of Russia’s aggressive actions in Ukraine.
India and Pakistan, with 172 (1.4%) and 170 (1.3%) warheads respectively, conducted their nuclear tests in Pokhran, Rajasthan, and Ras Koh Hills, Balochistan. The ongoing tensions between these two nuclear-armed neighbors, particularly over Kashmir, mean that their nuclear arsenals remain central to regional security. Their warheads are not deployed but are ready to be mobilized if a conflict escalates, making their standoff a constant flashpoint.
Israel, with approximately 90 warheads (0.7%), maintains a policy of ambiguity regarding its nuclear capabilities, which are believed to be stored at undisclosed locations. Israel has never confirmed any nuclear tests, maintaining strategic uncertainty. However, its nuclear arsenal is a significant factor in the Middle East, particularly in its complex relationship with Iran. The ongoing tensions between Israel and Iran, particularly over Iran’s nuclear program, highlight the potential for nuclear weapons to shape regional security. Similarly, the Israel-Palestine conflict occasionally raises concerns about the broader implications of nuclear weapons in the region, although Israel’s policy of ambiguity aims to keep its nuclear deterrent in the background.
North Korea, with 50 warheads (0.2%), has conducted several tests at the Punggye-ri site in Kilju, North Hamgyong. North Korea’s nuclear program is a major concern for global security, especially for its neighbors South Korea and Japan, and for the United States. The regime’s unpredictable nature and its nuclear capabilities add to the volatility of the Korean Peninsula.
In recent years, the Iran nuclear deal (JCPOA) and its breakdown have also brought nuclear weapons into the spotlight. While Iran does not have nuclear weapons, the tensions with the U.S., Israel, and other nations over its nuclear ambitions could potentially lead to a regional arms race, where nuclear arsenals would play a critical deterrent role.
These recent conflicts and tensions highlight the ongoing importance of nuclear weapons in global security. The presence of these arsenals, their deployment at strategic sites, and their historical testing reflect both the deterrence they provide and the significant risks they pose in today’s geopolitical landscape. The fear of nuclear escalation often serves as a critical factor in preventing conflicts from spiraling out of control, even as the international community continues to grapple with the challenges posed by these powerful weapons.
List of Countries with the total and deployed warheads
Information
Copyright: © 2024 Data Player
*Note: Hover or click on the bars to get the details.
Data source: SIPRI
This webpage provides information on Nuclear Warhead distribution by Countries using visualisation and uses various technologies for its functionality.
The following tools and technologies were used:
* HTML and CSS for the webpage structure and styling
* JavaScript for interactive features
* External data sources for statistics
You may like
Tears in Pahalgam – Terrorists Attacked Innocent People in India


The Rise of Asian Ethnic groups in 21st Century in the United Kingdom


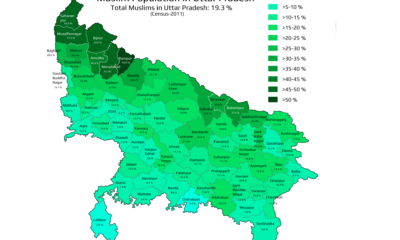
Mapped: What are the muslims population in Uttar Pradesh | State of India


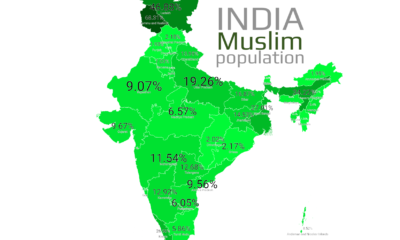
Mapped: What is Muslim Population in India by its State | Census 2011


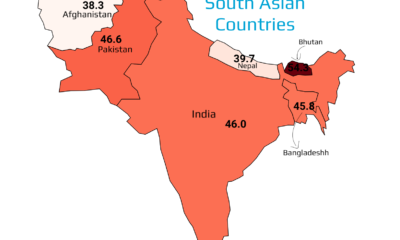
Mapped: Average Working Hours weekly by South Asian Countries in 2024
Millionaires are leaving their countries in 2024 why?
Trending

 Economy2 years ago
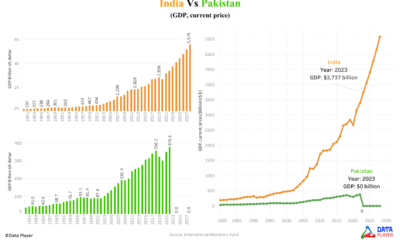
Economy2 years agoWhy Pakistan’s economy is drowning while India’s economy is touching the sky

 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoHighest number of software developers by country in the world 2023 by GitHub | Data Player

 Religion9 months ago
Religion9 months agoMapped: What are the muslims population in Uttar Pradesh | State of India

 Demographics10 months ago
Demographics10 months agoMapped: Average Working Hours by European Countries in 2024

 Demographics2 years ago
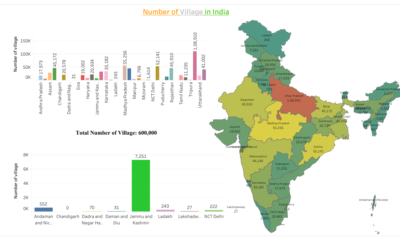
Demographics2 years agoWhat are the Number of Villages in India by its State and Union Territory

 Demographics2 years ago
Demographics2 years agoMassive population size by Indian states 2023

 Religion1 year ago
Religion1 year agoWorld’s Largest Religion in 2024 | Data Player

 Population10 months ago
Population10 months agoMuslim Population in London 2021 by Constituency: A Visual Guide