Economy
Trump’s 2025 Tariffs on India Explained: Full List, Dates, Products, and 50% Duty Impact
Economy
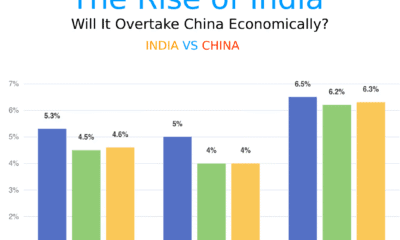
Is India Really a ‘Dead Economy’? A Deep Dive Into the Facts Trump Didn’t Mention
When Donald Trump recently called India a “dead economy,” it sparked global headlines and trended across social media. For many, this bold remark raised questions — is there any truth to it? Is India really falling behind, or is something else happening beneath the surface?
Economy
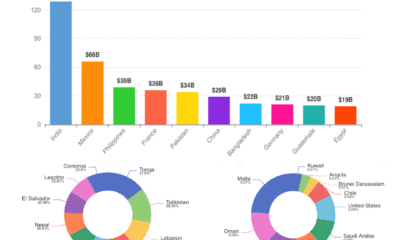
India’s Top Exports and Imports in 2023: What the World Buys and Sells with India
References
- Imf.org. (2021). Available at: https://www.imf.org/external/datamapper/NGDPD@WEO/ADVEC [Accessed 8 Jun. 2025].
- Financialexpress.com. (2025). Financial Express. [online] Available at: https://www.financialexpress.com/policy/economy-indias-gdp-doubles-in-10-years-to-4-3-trillion-to-outpace-world-with-105-rise-imf-3789035/ [Accessed 8 Jun. 2025].
- Desk, T.B. (2025). India to remain fastest-growing large economy for next three decades: Piyush Goyal. [online] The Times of India. Available at: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/india-to-remain-fastest-growing-large-economy-for-next-three-decades-piyush-goyal/articleshow/121505213.cms [Accessed 8 Jun. 2025].
- authorsalutation:|authorfirstname:EY|authorlastname:Global|authorjobtitle:Multidisciplinary professional services organization|authorurl:https://www.ey.com/en_in/people/ey (2025). India@100: reaping the demographic dividend. [online] Ey.com. Available at: https://www.ey.com/en_in/insights/india-at-100/reaping-the-demographic-dividend? [Accessed 10 Jun. 2025].
- Hudson Institute. (2025). India’s Demographic Dividend: Potential or Pitfall? [online] Available at: https://www.hudson.org/terrorism/indias-demographic-dividend-potential-or-pitfall-aparna-pande? [Accessed 10 Jun. 2025].
- Proteantech.in. (2019). Deciphering India Stack: Digital Public Infrastructure Explained. [online] Available at: https://proteantech.in/articles/understanding-india-stack/? [Accessed 10 Jun. 2025].
- Shetty, M. (2025). UPI transactions hit new high in May but cash still thriving. [online] The Times of India. Available at: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/upi-transactions-hit-new-high-in-may-but-cash-still-thriving/articleshow/121556499.cms? [Accessed 10 Jun. 2025].
- Wikipedia Contributors (2025). Production Linked Incentive schemes in India. Wikipedia.
- Venugopal, V. (2025). India electronics manufacturing secures $2.7bn boost. [online] @FinancialTimes. Available at: https://www.ft.com/content/def3e2bf-d2a6-44be-9876-4d71f0f0326c?.
- Nayar, S. (2025). India’s FDI Rise: A decade of decisive growth and global confidence. [online] The Economic Times. Available at: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/finance/indias-fdi-rise-a-decade-of-decisive-growth-and-global-confidence/articleshow/121618713.cms? [Accessed 10 Jun. 2025].
- Makeinindia.com. (2017). India’s Evolution: Tax Reforms, Digital Innovation, and Infrastructural Leap. [online] Available at: https://www.makeinindia.com/8-key-developments-india? [Accessed 10 Jun. 2025].
- Sharma, M. (2024). India Inc.’s challenge: Creating quality jobs amid informal work dominance. [online] Fortune India. Available at: https://www.fortuneindia.com/long-reads/india-incs-challenge-creating-quality-jobs-amid-informal-work-dominance/119441? [Accessed 10 Jun. 2025].
- Kumar, M. (2024). Let a million entrepreneurs grow! [online] arXiv.org. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.20709 [Accessed 10 Jun. 2025].
- Wikipedia Contributors (2025). National Policy on Skill Development. Wikipedia.
- MacDonald, M. and Spray, J. (2023). India Can Balance Curbing Emissions and Economic Growth. [online] IMF. Available at: https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2023/03/06/cf-india-can-balance-curbing-emissions-and-economic-growth.
- Journal of Public and International Affairs. (2025). Unlocking India’s Energy Transition: Opportunities, Challenges, and the Role of Cross-Subsidies. [online] Available at: https://jpia.princeton.edu/news/unlocking-india%E2%80%99s-energy-transition-opportunities-challenges-and-role-cross-subsidies.
- Wikipedia Contributors (2019). Economic liberalisation in India. [online] Wikipedia. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economic_liberalisation_in_India.
- Wikipedia. Tariffs in the Second Trump Administration. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tariffs_in_the_second_Trump_administration
- Times of India. India-US trade deal: Trump announces 25% tariff on India. Available at: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/india-us-trade-deal-trump-announces-25-tariff-on-india-plus-penalty-for-buying-energy-and-arms-from-russia/articleshow/122998698.cms
- Reuters. Trump imposes extra 25% tariff on Indian goods. Available at: https://www.reuters.com/world/india/trump-imposes-extra-25-tariff-indian-goods-ties-hit-new-low-2025-08-06/
- IndiaTimes. Donald Trump’s India tariffs set to hit US shoppers hard. Available at: https://indiatimes.com/trending/donald-trumps-india-tariffs-set-to-hit-us-shoppers-hard-phones-auto-parts-jeans-jewellery-to-get-costlier-665564.html
- Al Jazeera. Trump imposes 25 percent tariff on Indian goods over Russian oil. Available at: https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2025/8/6/trump-imposes-25-percent-tariff-on-indian-goods-over-russian-oil
- Economic Times. India reacts to 50% US tariffs. Available at: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/foreign-trade/trump-tariff-from-50-on-india-and-brazil-to-35-on-canada-heres-how-nations-stack-up-in-comparison/articleshow/123145315.cms
- Khandekar, N. (2025). India to remain fastest growing major eco with 6.5% growth in FY26: IMF. [online] The Economic Times. Available at: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/indicators/india-to-remain-fastest-growing-major-eco-with-6-5-growth-in-fy26-imf/articleshow/118649360.cms.
- World Bank (2023). Population, Total. [online] The World Bank. Available at: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.TOTL.
- CIA (2024). Median age – The World Factbook. [online] www.cia.gov. Available at: https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/median-age/country-comparison/.
- UN Comtrade. (2024). Available at: https://comtrade.un.org [Accessed 25 Jul. 2025].
- ITC Trade Map. (2024). Available at: https://www.trademap.org [Accessed 22 Jul. 2025].

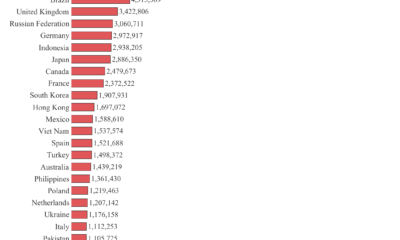
 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoHighest number of software developers by country in the world 2023 by GitHub | Data Player

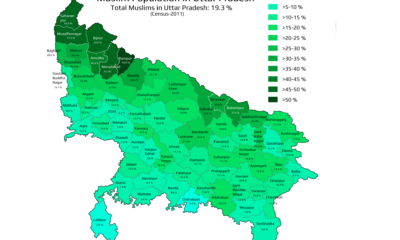
 Religion2 years ago
Religion2 years agoMapped: What are the muslims population in Uttar Pradesh | State of India

 Economy3 years ago
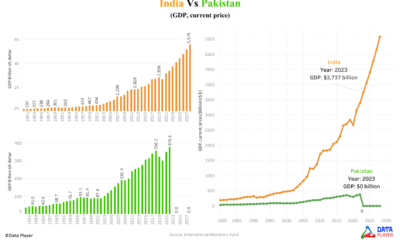
Economy3 years agoWhy Pakistan’s economy is drowning while India’s economy is touching the sky

 Demographics2 years ago
Demographics2 years agoMapped: Average Working Hours by European Countries in 2024

 Religion2 years ago
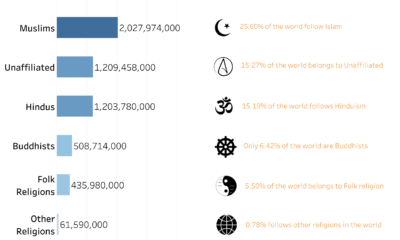
Religion2 years agoWorld’s Largest Religion in 2024 | Data Player

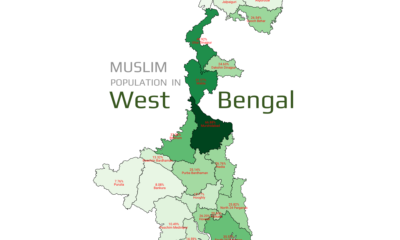
 Religion2 years ago
Religion2 years agoMapped: What is Muslim Population in West Bengal by District wise 2011

 Demographics3 years ago
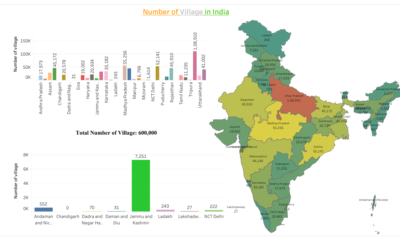
Demographics3 years agoWhat are the Number of Villages in India by its State and Union Territory

 Demographics3 years ago
Demographics3 years agoMassive population size by Indian states 2023